I’ve been working sporadically on an RPG system. Well, it’s not exactly a system. It’s more like my gloss on traditional fantasy gaming. Bits and pieces have already seen light (like the recent post on weapon abilities, and several trait ideas shared on G+, like this post on frenzy and this post on potions). I made good progress working on this over the past weekend, and now feel like I have enough of a real thing that I can start sharing parts and getting feedback from people. The text is still necessarily rather rough, so please excuse the unfinished edges.
This is a draft of the introduction. And for players of my OD&D game, no I don’t intend on changing anything about how we have been playing, though small things may creep in as optional rules now and again (like the weapon details).
Hexagram: A Fantasy Roleplaying Miscellany
Contained herein are a set of subsystems ready for use with any traditional class and level fantasy roleplaying game. Hexagram also constitutes a complete set of rules, with a particular philosophy, and may be played it as such.
This is what hexagram is about:
- Character advancement that tapers off, but never halts.
- No numerical inflation or numerical illusionism in game mechanics.
- Recognizable jargon where possible.
- Balanced choices through trade-offs.
- Lack of requirement for or benefit from system mastery.
- Fantasy archetypes, but with flexibility.
 |
| Image from Wikipedia |
Character advancement that tapers off, but never halts. Advancement of specific traits is limited, but there are often further traits available that have lesser or more specific impact within a given domain. Thus, character advancement should be logarithmic rather than linear, but there should always be something that a character can improve. Complexity should not be overwhelming, because the more specific traits only become relevant when the general traits have been maxed out, and are slowly introduced throughout play. This design also allows characters to remain at the human scale throughout their entire career, even as they accumulate magic, treasure, and political power.
No numerical inflation or numerical illusionism in game mechanics. (To be expanded upon later.)
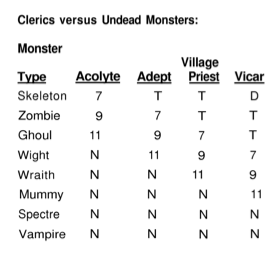
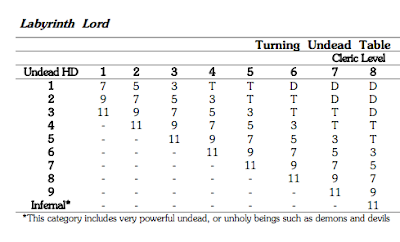
Recognizable jargon where possible. Hexagram character sheets should be mostly intelligible without needing to read any word of this rule set. The following is a valid Hexagram character: HD 3+1, AC 12 (leather), melee combat +3, floating AC bonus +3, sword, standard six ability scores, standard five saving throws, some adventuring gear (yes, the real character sheet would explicitly detail the last few things, but you get the idea). If you don’t already know what those things mean, they will be explained, but if you do, you should already feel at home.
Balanced choices through trade-offs. Though roleplaying is about immersing yourself in an imaginary reality and being awed the the wonder therein, it is also about solving problems. Potential solutions, at the mechanical level, should not generally be clearly optimal or suboptimal when divorced from specific situations. Game mechanical choices should always have interesting trade-offs, or they are not worth inclusion.
Lack of requirement for or benefit from system mastery. Options at any given point should never be overwhelming, but ultimate potential should be limitless (in terms of uniqueness if not character power). Choices are facilitated by random determination (dice rolling), but can also be guided by the player if desired. That is, random by default but not requirement. Limiting system mastery also keeps the character sheet small. It is intended to focus the game on problem solving and interaction with the diegetic environment, rather than management of character features.
Fantasy archetypes, but with flexibility. Beginning characters should be easy to create, but able to grow into unique variations on classic archetypes. All types of characters should be interesting to play at all levels. In addition, various character abilities can be gained at different times during a character’s career, depending on what makes sense for the particular campaign. This should allow some aspects of endgame content to be present throughout the entire game, rather than being cloistered in the high levels, since few games last that long. For example, sorcerers may brew potions at first level if they choose to focus on that activity, and some warriors may accumulate loyal follows immediately. In addition, characters are not limited to advancement within their primary archetypal domain, but advancement within that domain is easier and more direct.
Most game information (including potential character backgrounds and abilities) are presented in the form of random tables. There are several reasons behind this. The primary (practical) reason is to allow players to get started quickly. The secondary (theoretical) reason is the creative power of juxtaposition. Seemingly contradictory results can be the beginning of something memorable, and is related to the idea of synthesis out of thesis and antithesis.
It is possible to play Hexagram as a game built around character options (and it should work just fine that way) but it will really shine if you surrender to the dice and allow the character concept to emerge through play, rather than planning beforehand. That is why so much of the game (on both the referee and player sides) is built around guided randomness. A fully actualized Hexagram character should be a complex amalgam of player desires, setting opportunities acted upon, and dumb luck that nobody could ever see coming.
Even if that vision doesn’t do anything for you, there should be plenty of variant rules useable with your favorite class-and-level fantasy RPG.
The name Hexagram was not chosen arbitrarily. It represents several important aspects of this design. The hexagram, as a six-sided figure, embodies a limited number of short term possibilities. As a map division (from wargaming history), the hex also represents the starting point of a limitless and unconstrained journey. The juxtaposition of two triangles shows the reconciliation of opposites through synthesis. The number six has a lot of power and resonance. It is also the number of faces on the most common die, the number of the original set of ability scores, and the number of spell levels in the original game.
This document expects basic familiarity with tabletop roleplaying jargon (PC, NPC, referee, d20, etc) and also traditional fantasy gaming (HD, HP, XP, AC, etc). Here are a few other terms that either may not be in as wide usage or have specific meanings in the Hexagram context.
- Diegetic: within the game world. Something a PC could reason about.
- Extradiegetic: often used in film theory for things like music which only the audience can hear. In roleplaying, it means something that is for players to reason about (rather than PCs).
- Trait: some character aspect, ranked from 0 to 6. May often be used as a bonus to a die roll.
- T: As in, +T or -T. This is a variable intended to refer to a trait value. Use should be clear in context.
- Path: a collection of related traits in service of a broad archetype. All characters have a primary path.
- Path trait: a learned trait that belongs to a character’s primary path.
- Off-path trait: a learned trait that does not belong to a character’s primary path.
- Prototype: a small set of traits for starting characters in service of a narrow archetype.